In the intricate tapestry of human health, the link between obesity and various medical conditions continues to be a subject of extensive research. One such connection that has gained attention is the relationship between obesity and hernia.
Before delving into the connection, let's first understand what a hernia is. A hernia occurs when an organ or fatty tissue pushes through a weak spot or opening in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. The most common types of hernias are inguinal (groin), umbilical (belly button), and hiatal (upper stomach)


Obesity and Increased Intra-Abdominal Pressure:
Scientific studies have consistently shown that obesity contributes significantly to the development of hernias. The mechanism behind this connection lies in the increased intra-abdominal pressure that accompanies excess weight. Simply put, carrying excess fat in the abdominal region exerts additional pressure on the abdominal wall, making it more susceptible to herniation.
Research Highlights:
| Inguinal Hernias | Umbilical Hernias | Hiatal Hernias |
 Numerous studies, including research published in the "American Journal of Epidemiology," have found a positive correlation between obesity and the risk of developing inguinal hernias. The increased pressure on the abdominal wall weakens the muscles, creating an environment conducive to hernia formation. |  Obesity has been identified as a significant risk factor for the development of umbilical hernias. The excess fat accumulation in the abdominal region places strain on the abdominal muscles, particularly around the belly button, making it more prone to herniation. | 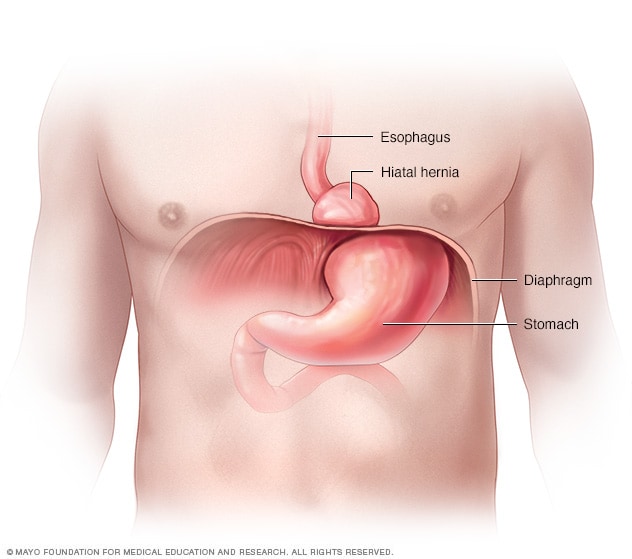 Obesity is also linked to the development of hiatal hernias, where a portion of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm. Research published in the "World Journal of Gastroenterology" highlights that increased intra-abdominal pressure due to obesity can contribute to the weakening of the diaphragmatic barrier, facilitating hiatal hernia formation. |
Preventive Measures:
By incorporating these preventive measures into daily life, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce the risk of hernia development, particularly in the context of obesity-
1. Maintain a Healthy Body Weight
2. Adopt a Balanced Diet
3. Regular Physical Activity
4. Proper Lifting Techniques
5. Posture Awareness
6. Quit Smoking
7. Manage Chronic Conditions
8. Regular Health Check-ups
9. Hydration
10. Weight Loss Support Programs
11. Consultation with Healthcare Professionals
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the scientific evidence supporting the link between hernias and obesity underscores the significance of maintaining a healthy weight for overall well-being. By making informed lifestyle choices, individuals can reduce the risk of hernia development and promote better abdominal health. This article serves as a guide to empower readers with knowledge, enabling them to take proactive steps towards a healthier, hernia-free life.
Did you find this topic helpful?